
In his report on The Periodic Law of the Chemical Elements in 1869, the Russian chemist Dmitri Mendeleev predicted the existence of several unknown chemical elements, including one that would fill a gap in the carbon family, located between silicon and tin. Prediction of germanium, "?=70" (periodic table 1869) However, synthetic soluble germanium salts are nephrotoxic, and synthetic chemically reactive germanium compounds with halogens and hydrogen are irritants and toxins. Similar to silicon and aluminium, naturally-occurring germanium compounds tend to be insoluble in water and thus have little oral toxicity. Some complex organic germanium compounds are being investigated as possible pharmaceuticals, though none have yet proven successful. Germanium is not thought to be an essential element for any living organism. Germanium is considered a technology-critical element.
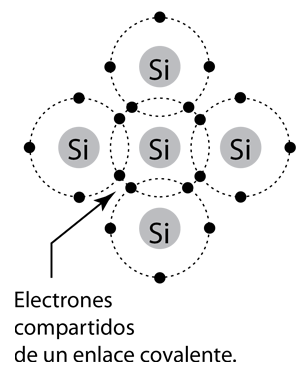
This element forms a large number of organogermanium compounds, such as tetraethylgermanium, useful in organometallic chemistry. Germanium compounds are also used for polymerization catalysts and have most recently found use in the production of nanowires. Presently, the major end uses are fibre-optic systems, infrared optics, solar cell applications, and light-emitting diodes (LEDs). Historically, the first decade of semiconductor electronics was based entirely on germanium. Today, germanium is mined primarily from sphalerite (the primary ore of zinc), though germanium is also recovered commercially from silver, lead, and copper ores.Įlemental germanium is used as a semiconductor in transistors and various other electronic devices. Winkler named the element after his country, Germany. Although the new element somewhat resembled arsenic and antimony in appearance, the combining ratios in compounds agreed with Mendeleev's predictions for a relative of silicon. Nearly two decades later, in 1886, Clemens Winkler found the new element along with silver and sulfur, in an uncommon mineral called argyrodite. In 1869, Dmitri Mendeleev predicted its existence and some of its properties from its position on his periodic table, and called the element ekasilicon. Germanium ranks near fiftieth in relative abundance of the elements in the Earth's crust. Like silicon, germanium naturally reacts and forms complexes with oxygen in nature.īecause it seldom appears in high concentration, germanium was discovered comparatively late in the history of chemistry. Pure germanium is a semiconductor with an appearance similar to elemental silicon. It is a lustrous, hard-brittle, grayish-white metalloid in the carbon group, chemically similar to its group neighbors silicon and tin.
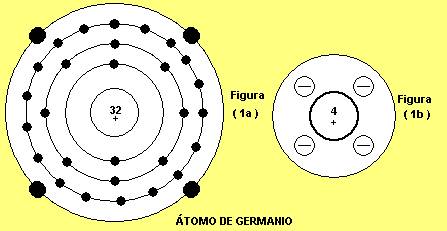

Germanium is a chemical element with the symbol Ge and atomic number 32.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
